Remeber few days ago, I was using BFS for tree traveral layer by layer, We initilize the levels = [], and for each layer of tree, we add another level. we use queue = deque([root,]) and while queue is not empty, we continue the loop. We use the lengh of the layer to do the popleft() and levels[level].append(node.val). The thing about graph here is that we need to keep track of the node we visited and then do the BFS for the not visited node. We may have two functions here to help us implement that.
Lets keep our logic clear with a small demonstration.
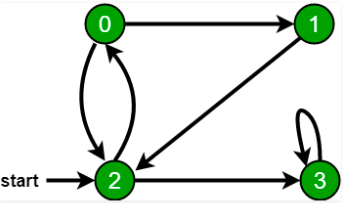 We start from the vertex 2 and when we reach vertex 0, keep in mind,2 is also an adjacent vertex of 0. That’s why we need to mark visited vertex. The path would be 2,0,3,1.
We start from the vertex 2 and when we reach vertex 0, keep in mind,2 is also an adjacent vertex of 0. That’s why we need to mark visited vertex. The path would be 2,0,3,1.
# Python3 Program to print BFS traversal
# from a given source vertex. BFS(int s)
# traverses vertices reachable from s.
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
# Constructor
def __init__(self):
# default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self,u,v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# Function to print a BFS of graph
def BFS(self, s):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False] * (len(self.graph))
# Create a queue for BFS
queue = []
# Mark the source node as
# visited and enqueue it
queue.append(s)
visited[s] = True
while queue:
# Dequeue a vertex from
# queue and print it
s = queue.pop(0)
print (s, end = " ")
# Get all adjacent vertices of the
# dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent
# has not been visited, then mark it
# visited and enqueue it
for i in self.graph[s]:
if visited[i] == False:
queue.append(i)
visited[i] = True
The detail is here
There is another coding example we can use to check the shortest path from A point to B point.
# function to find the shortest path
def find_shortest_path(graph, start, end, path =[]):
path = path + [start]
if start == end:
return path
shortest = None
for node in graph[start]:
if node not in path:
newpath = find_shortest_path(graph, node, end, path)
if newpath:
if not shortest or len(newpath) < len(shortest):
shortest = newpath
return shortest