There are several subjects in this topic.Access Control Lists, Mnagement Plane Security.
Here are a detailed list of router security policy:
- Password
- Authentication: local database or external AAA server,
- Access: SSH? HTTPS? Telnet?
- Services: Enabled services or should it be disabled
- Redundancy: If a router fails, is there a backup router to take over?
- Routing protocols: Authentication used for routing protocol.
Access Control Lists
Standard ACLs could match traffic based on source IP addresses and how extended ACLs could match traffic based source, destination ip address and a variety of other criteria such as port numbers.
Here are some examples we can use to utilize this protocol starting with ip access-list extended INFRASTRUCTURE !BLOCK PACKET FRAGMENT
deny tcp any any fragments
deny udp any any fragments
deny icmp any any fragments
deny ip any any fragments
!ALLOW NECESSARY ROUTING PROTOCOL
permit tcp <address-of-management-stations> any eq 22/161(SSH/SNMP)
permit icmp <address-of-management-stations> any echo
!DENY ALL OTHER TRAFFIC OR PERMIT ANY TRAFFIC
deny ip any <address-space-of-internal-network>(deny outside ip for inside)
permit ip any any
Last step, we should always apply it to the interface
interface Serial1/0
ip access-group INFRASTRUCTURE in
Secure Shell Versus Telnet
The issue with Telnet is that it sends data across a network in clear text. okay, lets give it a shot on GNS3.
AAA Every single time I encounter AAA, I remember one time I could not say the full name of it. I only knew Authentication and Authorization and have no idea of Accouting.
We are gonna talk about details of a AAA server.
- Authentication: check a user’s credentials to confirm he is who he claims to be
- Authorization: determine what that user is allowed to do
- Accouting: this service would collect and store information about a user’s login to keep an audit trail of what a user did on the network.
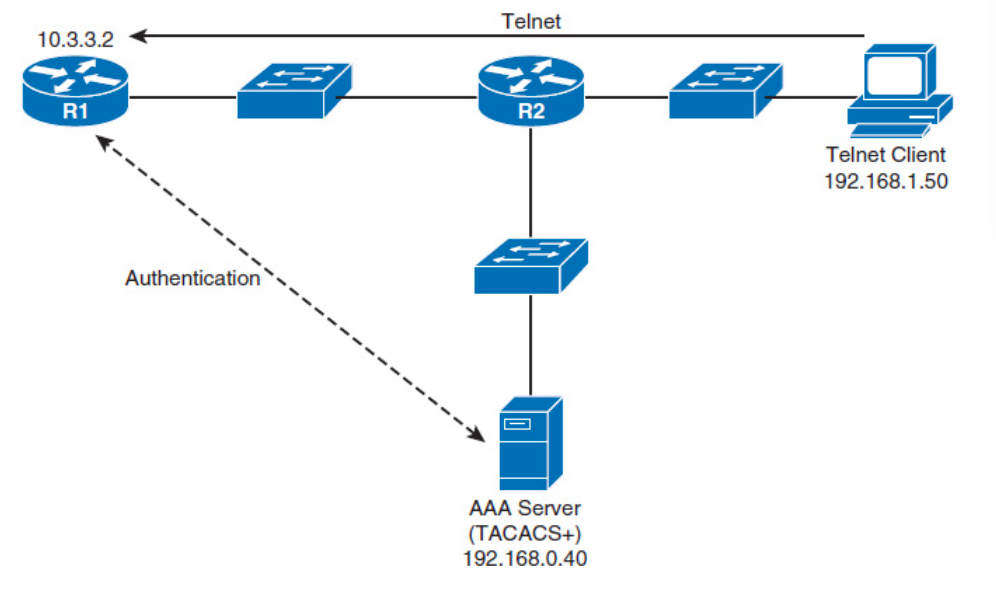 If the user pass the credential test, then he can telnet the remote router.
If the user pass the credential test, then he can telnet the remote router.
aaa new-model aaa authentication login ADMIN group tacacs+ local username kevin secret cisco #pick which server you are gonna use tacacs server CISCO-ACS address ipv4 192.168.0.40 key cisco #only limited person can access it line vty 0 4 login authentication ADMINThe aaa authenticaion login ADMIN group tacacs+ local command defines ADMIN, which attemps to perform authentication through a TACACS+ server. However, if the server is unavailable, the **local key would user local user database.
SNMP Security
SNMP is the standard for network management protocols. The picture shown below explains the simple interactions of SNMP.
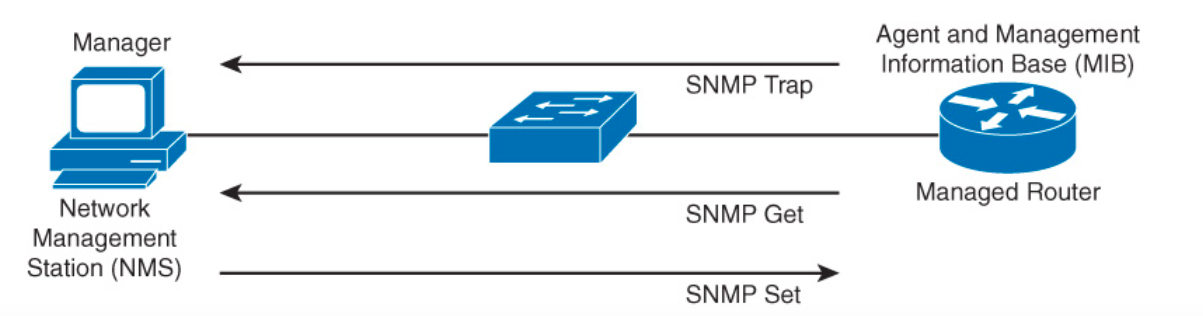 We have
We have GET to retrieve information from the router, We use SET to define what triggers an action on a managed device. Trap is just a message sent from a managed device to an SNMP manager, which can notigy the SNMP manager about a significant event that occured on the device.
NTP Authentication
The devices need to have a common point of reference for their time. This is mabe possible by Network Time Protocol, which allows one router to act as an NTP server. It uses a value called a stratum value to indicate the believability of a time source. Lower, more authoritative. 0 being the most authoritative.
So an attacker might use NTP as part of an attack. She might introduce her own NTP device into a network and advertise false time to network device. This could reuslt in misleading timestamp information apprearing in logs.
To mitigate the risk of having a rogue NTP server. We can totally configure NTP authentication.
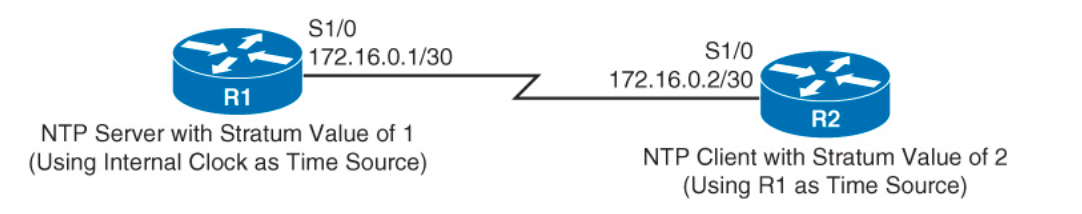
ntp authentication-key 1 md5 sfdasfdasfd
ntp authenticate
ntp trusted-key 1
ntp master 1
For R2, it would then add ntp server 172.16.0.1 key 1
That is all. Thank you for reading this.