It is a technology that is connected to switch Ethernet port.
To properly and effectively carry the traffic for a successful phone call, a combination of many switch features must be used. We need power for IP Phones as well as trunks link and the proper level of QoS for voice packet delivery.
Power over Ethernet
A Cisco IP Phone just need power to operate and power can come from two sources.
- An external AC adapter
- Power over Ethernet(DC) over the network data cable
The external AC adapter plugs in a normal AC wall outlet and provides 48v DC to the phone. But this would not work when there is power failure.
A more elegant solution is Power over Ethernet. 48V DC supply is provided to an IP Phone over the cable that is used for Ethernet connectivity. The DC power’s source is the switch itself.
How Power over Ethernet Work
There are two ways we can realize this function
- Cisco Inline Power:A Cisco-proprietary method
- IEEE 802.3af
I am not going to dive into this topic. The main focus of this article is Voice Vlans.
Most Cisco IP phones models contains a three-port switch, connecting to the uptsreaming switch, the user’s PC and the internal VoIP data stream.
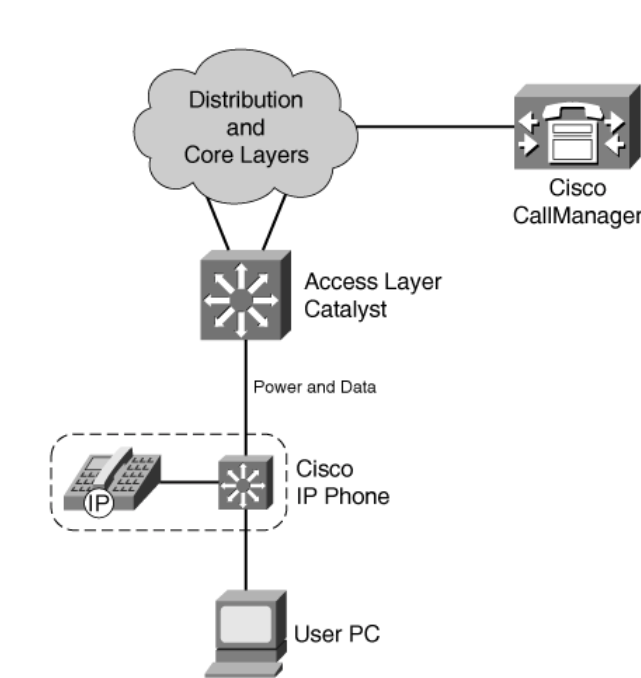
If you see the link between the switch and the IP phone, you can make it a single VLAN accees link or you can make it a 802.1Q trunk link. With a trunk, we can seperate the voice traffic and other user data.
The voice packets must be carried over a unique voice VLAN (known as the voice VLAN ID or VVID) or over the regular data VLAN (known as the native VLAN or the port VLAN ID, PVID). The QoS information from the voice packets also must be carried.
Switch(config-if)# switchport voice vlan {vlan-id | dot1p | untagged | none}
In here, we use voice vlan(tagged) and data untagged(native vlan). You can verfiy the configuration using spanning-tree command since STP runs with two instaces — one for Voice Vlan and another one for data Vlan.
By the way It can use IEEE 802.1p priority tagging to give voice traffic a higher priority and forward all voice traffic through the native (access) VLAN 0.
config t
int gi0/0
trust-device cisco-phone
switchport voice vlan dot1p
#By default, the Cisco IP Phone forwards the voice traffic with an IEEE 802.1Q priority of 5