Last time, I studied port-security and authentication on switch. This time we are going to focus on some typical attacks that can be operated on switch.
Before I address the attack on DHCP server, lets get it clear how pc interacts with the DHCP server.
It has four steps in total.
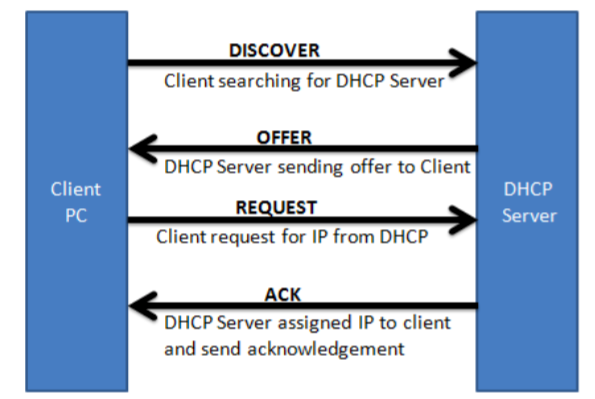
A DHCP server normally provides all the information that a PC may need to operate on a network. For example, the client may receives an IP address, a subnet mask, a default gateway and DNS addresses, and so on.
Suppose when the PC broadcast a DHCP request and the rogue server could send a carefully crafted DHCP reply with its own IP address as the default gateway.
So, think about it, When the client receives the reply, it begins using the spoofed gateway address. Packets destined for address outside the local subnet then go to the attacker’ machine first. YES, the fake one can still forward the packet but it will examine every packet it intercepts. This is a typical MAN in the middle attack.
When DHCP snooping is enabled, switchports are categorized as trusted or untrusted. Legitimate DHCP servers can be found on trusted ports and that is all.
Any DHCP replies coming from an untrusted port are discarded because they must have come from a rogue DHCP server. In addtion, the offending switchport will be in the state of errdisable.
Configuration ~~ Switch(config)#ip dhcp snooping Switch(config)#ip dhcp snooping vlan vlan-id [vlan-id] ~~ In default, all the switchport are untrusted until you point out to the port ‘connected’ to the DHCP server.
interface gi 0/0
ip dhcp snooping trust
For untrusted, it can still send out DHCP request and unlimited rate is accepted. Thats why you will need the command shown below:
Switch(config)#interface type mod/num
Switch(config-if)#ip dhcp snooping limit rate rate
Scenario Interface f0/35 and f0/36 using access vlan 36 while a DHCP server is located on the gi0/0 uplink.
ip dhcp snooping
ip dhcp snooping access vlan 36
int range f0/35 -36
ip dhcp snooping limit rate 3
int gi 0/0
ip dhcp snooping trust
Since DHCP snooping dataabse can keep track of the host that sends out a DHCP request. In this case, switch actually learns the MAC and IP addresses of hosts that use DHCP
Dynamic ARP Inspection
Oh, we need arp so much and I have to say my new housemate is on fire. shame on myself, but living with someone pretty actually can make life more satisfied.
Hosts usually use the Address Resolution Protocol to resolve unknown MAC address whent the IP address is known. A host would literally broadcast an arp request that contains the IP address of the target in question.
However, suppose that an attacker could send its own craafted ARP reply when it overhears an ARP request being broadcast. Packets will be sent to the attacker instead of another host or the default gateway.
The attack is known as ARP poisoning and it is considered to be a type man-in-middle attack. Cisco switch can use DAI to help mitigate this type of attack.
It is similar to DHCP snooping. All switch ports are classified as trusted or untrusted. The switch intercepts and inspects ALL ARP packets that arrive on untrusted port.
This is important that switch can gather trusted ARP information from statically configured entries or from dynamic entries in the DHCP snooping database!!! Now, you can see the importance that we keep track of anything in our life. Avoid malicious attack.
Switch(config)#ip arp inspection vlan vlan-range
By default, all switch ports associated with the Vlan are considered to be untrusted.
Switch(config)#interface type mod/num
Switch(config-if)#ip arp inspection trust
But what if we have hosts with statically configured IP address information, there will be no dhcp message that can be inspected. Instead, you can configure an ARP access list that defines static MAC-IP bindings.
When ARP replies are intercepted, their contents are matched against the access list entries first. If no match is found, the DHCP snooping bindings database is checked next.
EXAMPLE DAI are enabled for all switchport associated with VLAN 104 on an access-layer switch. The uplink is considered to be trusted.
Switch(config)#ip arp inspection vlan 104
Switch(config)#arp access-list StaticARP
Switch(config-acl)#permit ip host 192.168.1.10 mac host 0006.5b02.a841
Switch(config-acl)#exit
Switch(config)#ip arp inspection filter StaticARP vlan 104
Switch(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/1
Switch(config-if)#ip arp inspection trust
More details about switch, click here