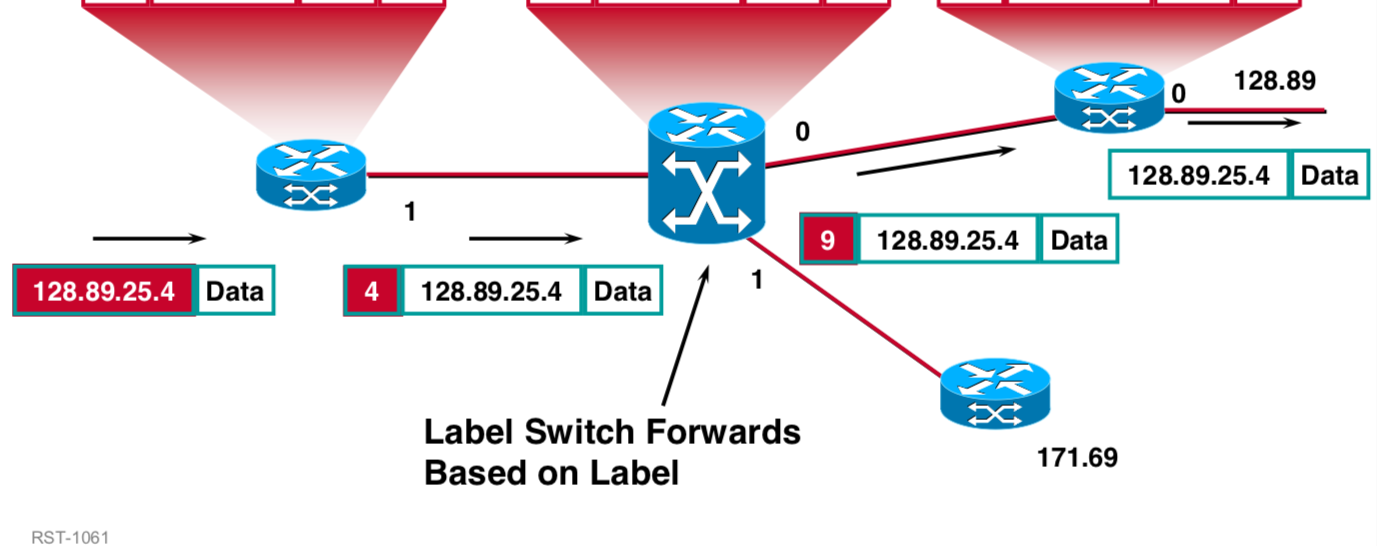
Routers usually make decisions based on destination IP addresses. With MPLS, the router no longer look at the destination IP address to make decisions. They are looking at MPLS label to decide what to do.
There are several advantages that MPLS owns:
- peer-to-peer model securing L3VPN
- BGP-free core, core routers make decisions base on labels
- Unified network infrastructure
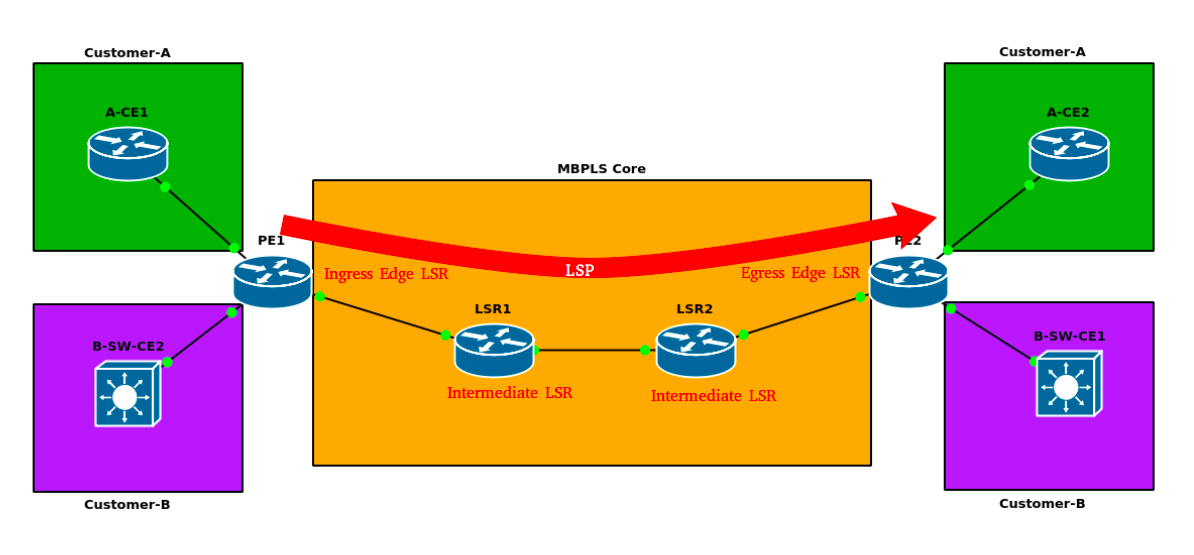
MPLS Terminology
The most important ones are Label Switch Routers(LSR), it can be ingress edgeLSR who receives regular IP packet and then push labels before forwarding the packet into MPLS network. Or it can be a intermediate LSR doing push,pop and swap.
Next, you need to know Label Distribution Protocol which enables LSRs to exchange label binding information.
PS: Ping works fine in MPLS environment but there are so many underlying issues .If an END to END ping fails, it can be unclear where the exact problem is (MPLS network, IGP? Firewall?). That is why a special MPLS ping utility was developed.
Let’s do some configuration then.
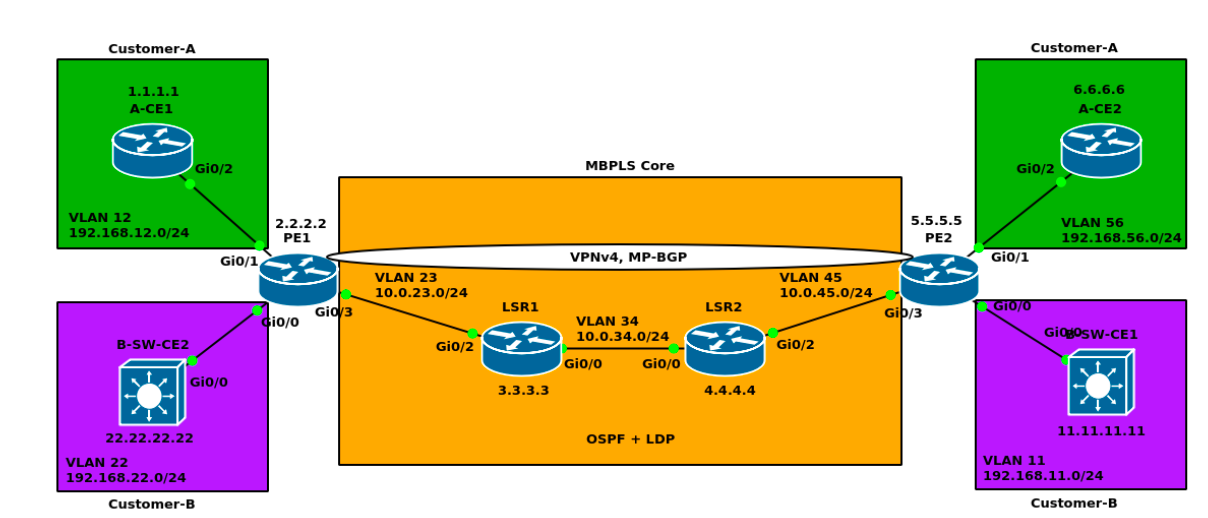 I would only do one side and then the other side is the same configuration.
Host CE1
I would only do one side and then the other side is the same configuration.
Host CE1
hostname A-CE1
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2.12
encapsulation dot1Q 12
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
PE1
hostname PE1
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0.22
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1.12
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/3.23
encapsulation dot1Q 23
ip address 10.0.23.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
passive-interface default
no passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/3.23
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.23.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
Here, we notice that the interface facing the customer edge(CE) is not configured!!!
LSR1
hostname LSR1
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0.34
encapsulation dot1Q 34
ip address 10.0.34.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2.23
encapsulation dot1Q 23
ip address 10.0.23.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
router ospf 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
passive-interface default
no passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0.34
no passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/2.23
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.23.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.34.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
We use routing protocol to establish reachability to destination networks (Normally we would use ospf). Dont forget to advertise loopback, we would use that for mpls.
For those mpls configuration
mpls ip
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0
mpls label range 300 399
interface gigabitEthernet 0/2.23
mpls ip
interface gigabitEthernet 0/0.34
mpls ip