We often need to discover how the performance of an application is affected when the system is under certain types of loads. This means artificial load must be re-created.
Before that, I need to address the difference between /dev/zero and /dev/null, /dev/zero produces a continuous stream of NULL(zero value) bytes while /dev/null produces no output. So, we could say we use /dev/zero to create dummy files or swap.
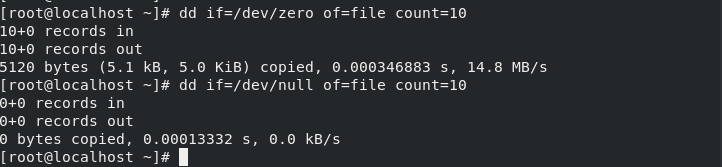
Disk
We will create disk I/O by firstly creating a file, and then use a for loop to repeatedly copy it.
- Generate a 1GB of file
dd if=/dev/zero of=file bs=1M count=1024 - a loop that runs 10 times
for i in {1..10}; do cp file file1; done
The orginal post also mention how to drain CPU and RAM. link